
This two-hour webinar will assume knowledge of the MMPI-2-RF and will provide an overview of the similarities and differences between the MMPI-2-RF and MMPI-3, including a description of the rationale for and methods used to develop the MMPI-3. **Please note: prior knowledge of the MMPI-2-RF is essential for this bridging workshop Webinar Link: This webinar can be accessed as an on-demand recording via this link Presenter: Professor Martin Sellbom, University of Otago It does take training and knowledge to get a psychological accuracy that is useful for employment or court use of the MMPI.Transitioning from MMPI-2-RF to MMPI-3 in Psychological Practice The accurate interpretation of your MMPI results is one of the reasons those who are trained and qualified to administer the MMPI tests like to strongly discourage people attempting to do it themselves. Problem areas with a score below 30 and over 70ģ) Compare your score to the average T score.Ĥ) Look at what the test (and thus the T score) is measuring. This will come from the results of the testĢ) Look at your T score on the normal distribution.Īverage is any score between 40-60, A slight issue would be between 30-40 or 60-70.
#Mmpi 2 rf interpretation worksheet how to
How to Read your Scoreġ) Identify the T score you want to interpret.

It is useful for expressing the variability of a population, standard deviation is commonly used to measure confidence in statistical conclusions. A low standard deviation indicates that the data points tend to be very close to the mean, whereas high standard deviation indicates that the data points are spread out over a large range of values. It shows how much variation or “dispersion” exists from the average (mean, or expected value). Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. Ideally, the MMPI-2 is being administered as a part of a battery of psychological tests, so that other testing can either confirm or deny the hypotheses the MMPI-2 may suggest. For instance, we might expect a higher score in Hypomania (a measure of energy levels) in a teen, but it might be more unusual to see such a score in a senior citizen. Like all psychological interpretation, scores are analyzed in context of the individual being tested - not in a vacuum.

Most people with personality or mental health issues will usually have only one codetype, or a single codetype with a spike on a third scale. People with little or no psychopathology or personality concerns will not reach significance for any particular codetype. For instance, a 2-3 codetype (meaning that both Scale 2 and Scale 3 are significantly elevated) suggests significant depression, lowered activity levels and helplesness furthermore the person may have become accustomed to their chronic problems and often have physical complaints.ĭozens of clinical codetypes are well-known and understood, as well as T scores that “spike” on a single Scale (such as a “Spike 4”, which would be a sign of a person who shows impulsive behavior, rebelliousness and poor relationships with authority figures). Throughout the years and over numerous research studies, a set of standard clinical profiles have emerged on the MMPI-2 which professionals call “codetypes.” A codetype is simply when two scales demonstrate significantly high T scores, with one being higher than the other. Anything above 65 and anything below 50 is considered clinically significant and open for interpretation by the psychologist.
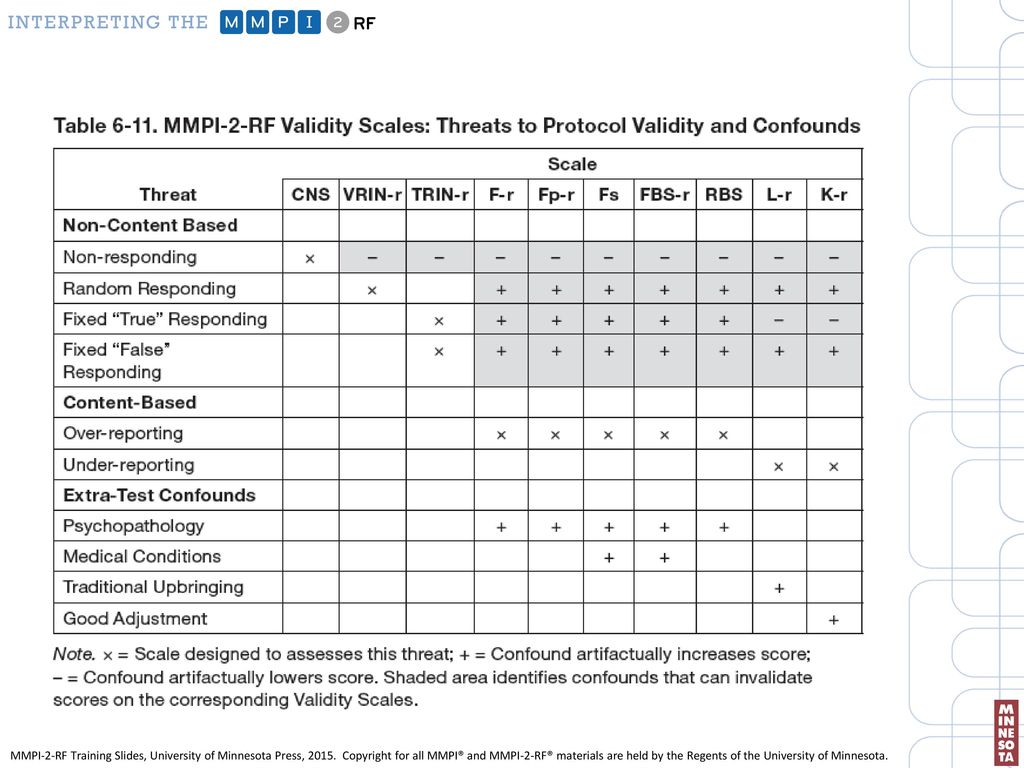
The “normal” range of T scores is from 50 to 65. Scores are converted to what are called normalized “T scores” on a scale ranging from 30 to 120. After the MMPI-2 is taken and scored, an interpretive report is constructed by the psychologist.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
